Endocannabinoid system 101
The endocannabinoid system is a biological system that your body needs to maintain homeostasis or balance. It’s known to regulate multiple bodily functions that are vital for good health and wellbeing. This system plays a major role in keeping you healthy and is the main system upon which cannabis acts to provide therapeutic benefits.
If you’re thinking about starting a regime that includes cannabis, you must understand how the endocannabinoid system works and how cannabis interacts with your body. In this article, you’ll learn about the endocannabinoid system’s (ECS) role, why the ECS is important, and how cannabis works with the ECS. We spoke with Dr Matty Moore, a GP from WA, to learn more about the ECS.
Here are the topics we cover:
- What is the Endocannabinoid System?
- Parts of the Endocannabinoid System
- How does the Endocannabinoid System work?
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The ECS is an internal biological system that is made up of internally produced cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) and receptors (cannabinoid receptors) that help regulate and maintain homeostasis within your body.
Cannabinoids are the name given to all chemical substances that help communicate and join cannabinoid receptors and the brain.
The ECS plays an essential role in our central nervous system and immune systems. People talk about the ECS as being responsible for functions such as: Eat, Sleep, Relax, Forget, and Protect. Research shows that it regulates about 15 major bodily functions. And, we can augment the system or improve these processes by influencing them to run even better.

There are two ways you can upregulate your endocannabinoid system. You can optimise certain natural activities like eating foods, exercising and doing stress-relieving activities like meditation or yoga and/or you can consume exogenous plant cannabinoids (phytocannabinoids via cannabis). The two best-known phytocannabinoids are delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD).
Everything you do to enhance the functionality of your ECS should be with moderation in mind. This is because the ECS helps maintain balance.
Parts of the ECS
The ECS is made up of two parts:
- Cannabinoid receptors
- Cannabinoids
To explain how the ECS works, we’ll first explain the parts individually.
Cannabinoid receptors
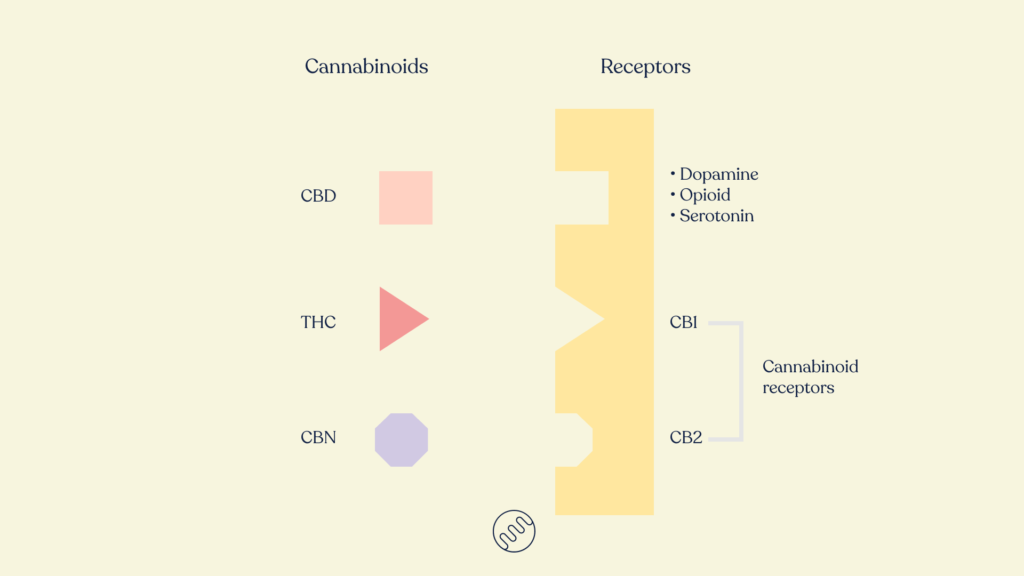
There are two types of cannabinoid receptors in our bodies: the CB1 receptor and the CB2 receptor.
CB1 receptors are located throughout the nervous system. They sit on the part of the nerve that communicates with the next nerve. When CB1 receptors are activated, they slow the release of neurotransmitters. Scientists think that this slowing of transmissions could help explain why cannabis can have an anticonvulsant effect.
CB2 receptors are mostly found in the immune system, specifically in organs and cells involved with a response. Some examples of CB2 receptor locations are the liver, the spleen, monocytes (cell), macrophages (cell), B cells and T cells. As an example, in autoimmune hepatitis, the CB2 receptor activation reduces inflammatory messengers called cytokines. And, as another example, it’s through the CB2 receptors that neurodegeneration and blood-brain barrier damage is slowed in traumatic brain injuries.
Types of cannabinoids
There are two main types of cannabinoids:
- Endocannabinoids
- Phytocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids is the shortened word for endogenous cannabinoids or cannabinoids from within the body. Our body makes these cannabinoids naturally. Each person’s body may make different amounts and have an abundance or deficiency of these cannabinoids. There are two major endocannabinoids that our bodies make: Anandamide and 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
Anandamide is Sanskrit for bliss and is best known to be responsible for the feeling of the “runner’s high’ after exercise. It is a ligand for the CB1 receptor, meaning it binds to the receptor and creates or enhances an effect. 2-AG is an agonist (activator) of the CB1 receptor and has high concentrations in the brain. 2AG has been associated with the following therapeutic properties: reduced pain, antiemetic (reduced vomiting), appetite stimulation and the inhibition of tumour growth.
Phytocannabinoids
Phytocannabinoids are plant (phyto) cannabinoids naturally occurring in various plant species. The term, however, is most popularly associated with cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. There are hundreds of cannabinoids found in cannabis; The most popular and well-known chemicals are CBD and THC, followed by CBN, CBC and CBG.
These phytocannabinoids have a similar chemical structure to our endocannabinoids and therefore help internal processes when ingested.
Cannabinoid & ECS interaction
How does the endocannabinoid system work?
Endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids bind and interact with each other and many other receptors in the body. Cannabinoids work with the receptors like lock and key. The receptors are like locks, and the cannabinoids are the keys. Once cannabinoid receptors are engaged, they set off a process to slow down the nerve signal. For comparison, cannabinoids can act as a dimmer on a light switch or a thermostat on an AC.
The ECS regulates the creation and sending of a message from one nerve to another. Different cannabinoid receptor interactions have different impacts on the body and help regulate several critical functions. We’ll now cover THC and CBD to give you a stronger understanding of how the ECS and cannabinoids work.
THC and your ECS
THC is the most abundant of the phytocannabinoids and is an important therapeutic agent with a wide range of medicinal properties. People often think of THC as being the psychoactive component of cannabis. The psychoactive effects of THC result from the activation of the CB1 receptors in the brain. The brain-receptor activity happens throughout the cortex, midbrain, cerebellum and spinal cord. Because THC works directly on the receptors, using too much THC can actually flood the receptor creating a tolerance. This is one of the reasons you may need a THC tolerance break if you use THC frequently or at very high doses.
While THC can increase anxiety, slow reaction times and impair memory when used too frequently or at too high a dose, it also has many positive effects, such as pain relief. It may improve cancer-related symptoms like increasing appetite and reducing nausea and vomiting, and improving sleep.
CBD and your ECS
CBD is the second most abundant phytocannabinoid in cannabis and is a non-impairing cannabinoid. It is thought to have the ability to decrease some of the negative side effects of THC. CBD has a higher affinity to bind to the CB2 receptor and does not bind to the CB1 receptor like THC.
CBD is also thought to interact with other receptors in your body, including the opioid, dopamine, and serotonin receptors. Because of its unique interaction with multiple receptors, CBD is known to improve the immune system and reduce inflammation, pain, depression, anxiety, and help with addiction.
Conclusion
Keeping your ECS at peak performance is important to your overall health. The ECS helps maintain balance within your body by using cannabinoids and receptors to send messages and modulate internal processes.
You can upregulate your ECS naturally or by supplementing it with phytocannabinoids, including cannabis. CBD and THC have different effects and work on different parts of the body. The two main cannabinoids have overlapping but varying therapeutic qualities.
Cannabis products can help optimise your ECS; however, like all other supplements or drugs, too much can hurt your health and wellbeing. Medical cannabis products come in various forms with different cannabinoids, terpenes and other chemicals that may help upregulate your endocannabinoid system.
And, while generally well-tolerated and safe, cannabis doesn’t work for everyone. If you think medicinal cannabis is right for you, then talk to your GP or specialist.



